Starting a company and raising capital can feel like navigating a complex maze. One crucial tool often overlooked is the pro forma cap table. This isn't just a spreadsheet of numbers; it's a dynamic roadmap showing your company's ownership structure, projecting how it will evolve with funding rounds and employee stock options. Mastering your pro forma cap table is key to attracting investors and ensuring fair compensation for everyone involved. This guide will equip you with the knowledge to build and manage yours effectively.
Understanding the Basics: Who Owns What?
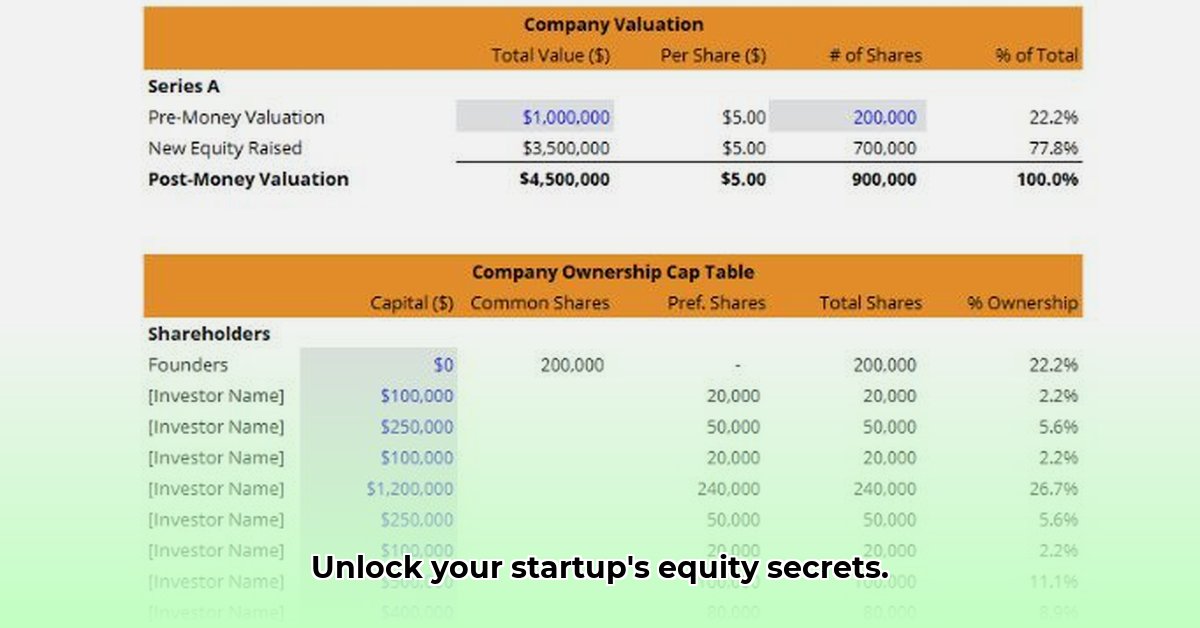
A pro forma cap table projects your company's ownership structure at a specific point in the future. It's a forecast, a snapshot showing who owns what percentage of your company, anticipating the impact of future funding rounds and employee stock options. Think of it as a financial model predicting ownership, helping you visualize the effects of dilution (the decrease in ownership percentage as new shares are issued). Why is this important? Because understanding potential dilution allows you to make informed decisions about fundraising and team compensation.
Imagine building a house without blueprints. A pro forma cap table is your blueprint for your company's equity, guiding its growth and financial stability.
Your Step-by-Step Guide: Building Your Equity Map
Building a pro forma cap table might seem intimidating, but breaking it down into simple steps makes it manageable.
Step 1: Documenting Your Current Ownership
Begin by listing all current shareholders and their ownership percentages. For example, if you and a co-founder each own 50%, that’s your starting point.
Step 2: Understanding Stock Types
Familiarize yourself with common and preferred stock. Common stock usually grants voting rights proportional to ownership. Preferred stock often comes with special rights, such as receiving investments back first in a sale. Understanding these differences is crucial for strategic fundraising.
Step 3: Forecasting Funding Rounds
Project the amount you plan to raise in future funding rounds and the company's valuation at each stage. Remember, these are educated guesses; refine them as you progress.
Step 4: Calculating Dilution
This involves using your projected valuations and funding amounts to calculate how much ownership will be diluted with each funding round. While dilution is inevitable with growth, understanding its extent is key.
Step 5: Incorporating Employee Stock Options
Employee stock options are strong incentives, but remember they will dilute existing ownership. Accurately estimate the number of options and their impact.
Step 6: Organize Your Data
Use a spreadsheet or dedicated cap table software for organization and accurate tracking. Clear labeling is crucial for easy updates and to minimize errors. Isn't it amazing how easily a misplaced decimal can affect your entire plan?
Step 7: Regular Review and Updates
Your pro forma cap table is a dynamic tool; update it regularly to reflect your company's evolving situation. Regular updates maintain accuracy and allow for proactive strategy adjustments.
Potential Pitfalls to Avoid
While straightforward, building a pro forma cap table has potential pitfalls:
1. Unrealistic Expectations: Overly optimistic projections lead to inaccuracies. Use realistic estimates based on market trends and your business's progress.
2. Spreadsheet Errors: Simple errors in formulas can have significant consequences. Double-check your work, or better yet, use specialized software.
3. Ignoring Legal Considerations: Consult legal counsel to ensure compliance with regulations. This is especially important for substantial funding rounds.
When to Seek Expert Help
While this guide provides a strong foundation, professional guidance is beneficial for complex scenarios. Attorneys specializing in startup law and financial advisors can help navigate complex equity structures and ensure legal compliance.
“A well-managed cap table is a cornerstone of a successful startup,” says Anya Petrova, Partner at Venture Capital Firm. "Ignoring its significance can lead to significant legal and financial challenges down the line."
Your pro forma cap table is more than a document; it's an essential tool for navigating the complexities of startup growth. Use it wisely.
How to Handle Complex Preferred Stock Structures
Preferred stock comes with preferential rights, such as preferential dividends and liquidation preferences. Understanding different classes of preferred stock and their specific terms is crucial for accurate cap table management. This is where professional guidance often becomes invaluable.
Key Takeaways:
- Pro forma cap tables are essential for projecting future ownership and dilution.
- Precise valuations and realistic assumptions are paramount.
- Understanding preferred stock structures is vital for accuracy.
- Specialized software simplifies the process and reduces errors.
- Legal and financial advice ensures compliance and optimal strategies.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Complex Structures
- Start with the Basics: Begin with your initial share structure.
- Add Funding Rounds: Include details of each funding round, including share issuance, price per share, and stock type.
- Incorporate Options and Warrants: Factor in potential future dilution.
- Account for Vesting Schedules: Reflect employee stock option vesting schedules.
- Handle Preferred Stock Features: Document all features, including liquidation preferences and participation rights.
- Use Specialized Software: Automate calculations using dedicated software.
Navigating Complex Scenarios
- Multiple Classes of Preferred Stock: Each class needs to be accounted for individually.
- Anti-Dilution Provisions: These protect investors from dilution; account for their impact.
- Liquidation Preferences: Determine the order and amount of distributions in case of a sale.
Avoiding Pitfalls: Accuracy and Transparency
Accuracy is crucial; incorrect projections can lead to investor disputes. Regularly update your cap table to reflect changes and maintain transparency with your investors.
Pro Forma Cap Table Template Example
| Security Type | Number of Shares | Price Per Share | Total Value | Ownership (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Founder Shares (Common) | 1,000,000 | $0.01 | $10,000 | 50% |
| Series A Preferred | 500,000 | $1 | $500,000 | 25% |
| Employee Options | 100,000 | N/A | N/A | 5% |
| Series B Preferred | 250,000 | $2 | $500,000 | 12.5% |
| Total Outstanding | 1,850,000 | $1,010,000 | 100% |
Note: This is a simplified example. Actual cap tables can be much more complex.